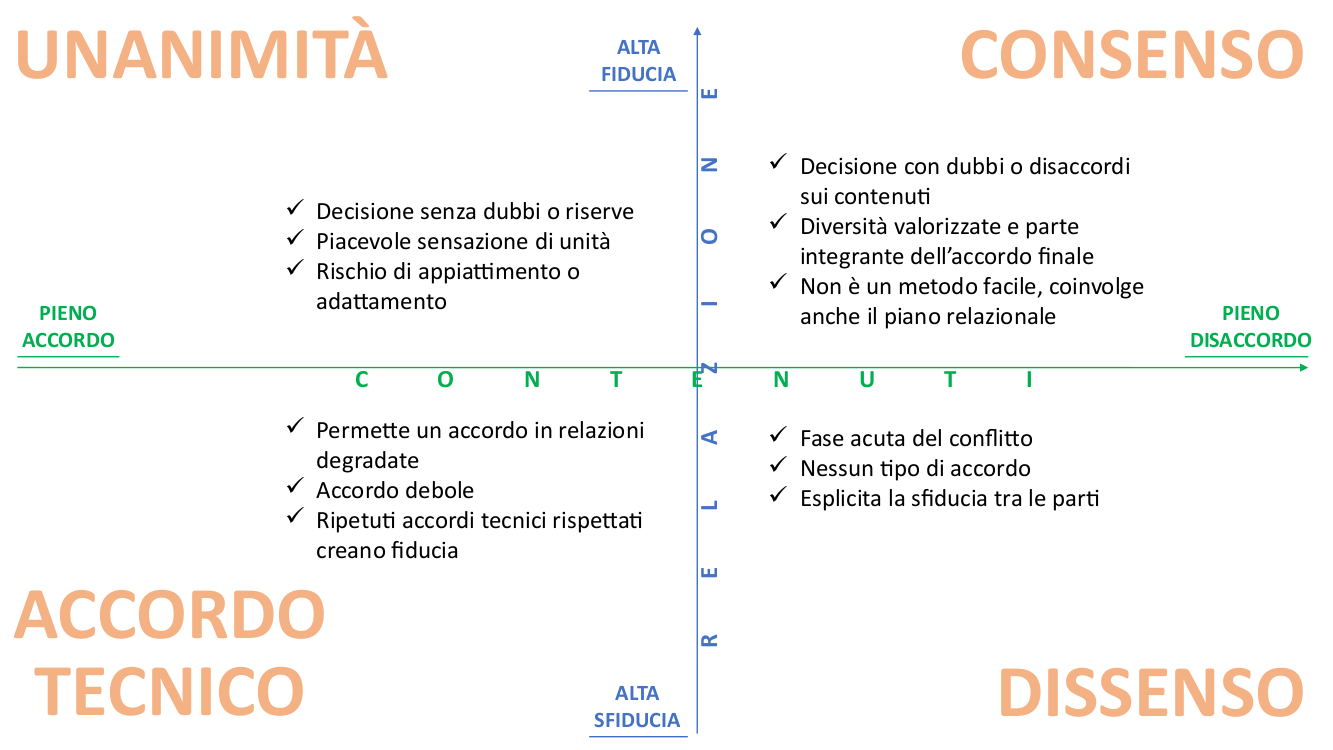
XMPP is an open instant messaging protocol based on XML. XMPP architecture is similar to emails; Anyone can make their XMPP server and do not identify central servers. In general, using XMPP is a little less comfortable and immediate than the typical experience of a commercial app, but this is due to the fact that it is an open protocol and not a service provided by a company.
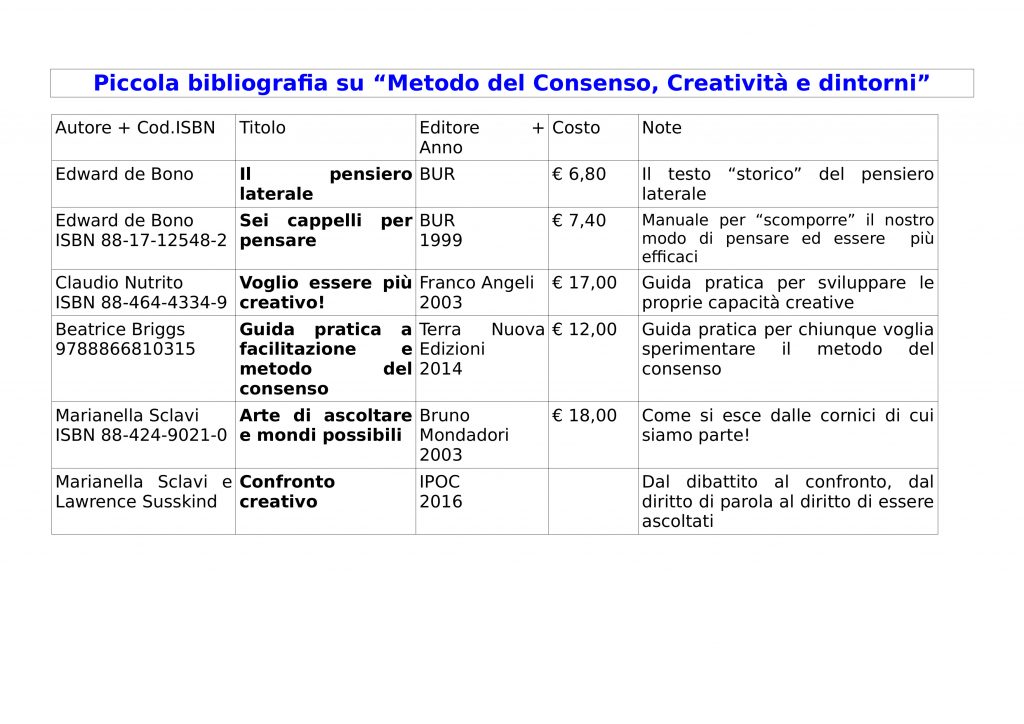
1. An email box on the autistic server
2. An XMPP client
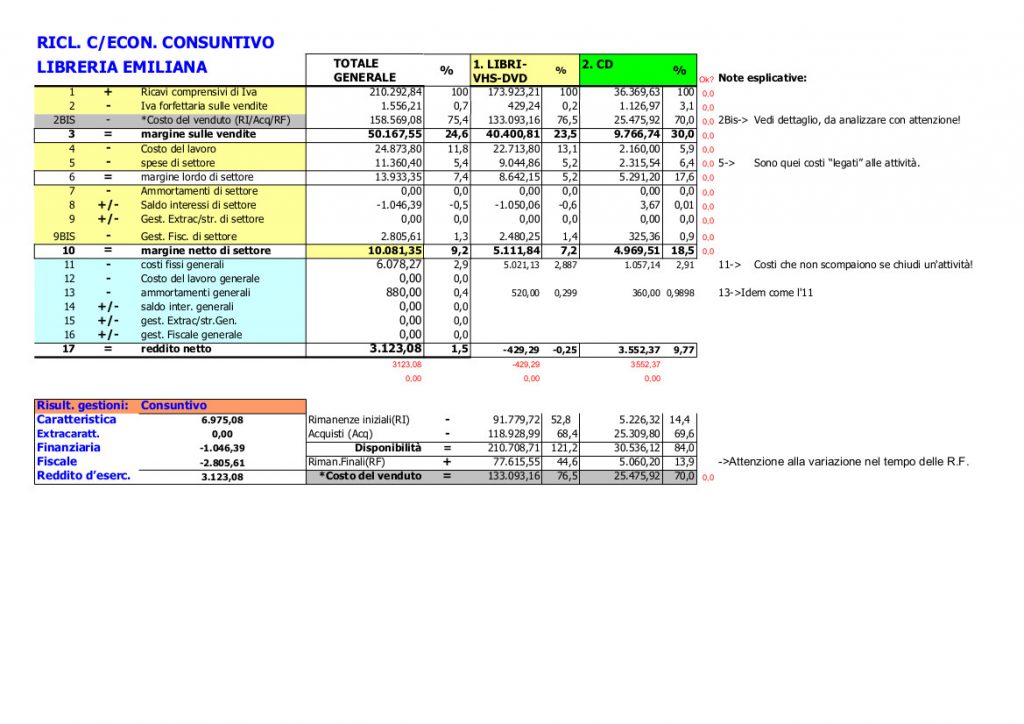
3. Sign In on the client
4. Add a contact
1. Create an email Autistici (if you have already jump it!)
On autistici.org servers (they are comrades!) the XMPP architecture is installed and if you create an email on their server you can start using XMPP. The emails created with the “autistici/inventati” services are anonymous, through them it is not possible to get to your identity. I therefore recommend that you do not use your true names and surnames for the email.
The procedure for requesting a new email is very simple:
1) Go to https://services.authensum.org/new-request/stage1
2) “E -mail – Single Mailbox” should already be selected, then click “Continue”
3) Choose the email, then “continuous”
4) Now a form will open where you can write why you want an autistici email. I recommend writing something sensible, it is truly read by people and considered what you write.
5) Once this is done, you will be returned a link (to be saved, if you lose it you have to get rinted from the beginning) where in a few days you will be communicated the activation of your email. Then save yourself this link somewhere and go back to us the next day or the next one.
2. Install an XMPP client
There are a myriad of software to use XMPP.
For Android I recommend “Conversations”, to install it for free you must download it not from the play store, but you can download and install the apk that you find here (https://f-droid.org/packages/eu.siacs .conversations/), or from F-Droid.
For Windows, Mac or Linux I recommend Gajim (https://gajim.org/)
For iOs Monal (also on Mac)
For Browser Conversejs https://conversejs.org/fullscreen.html
Other clients: Dino for Linux, Cheogram for Android, etc. .. Then maybe you can also find better!
3. Login
4. Now you can chat with someone
To chat with another person, just let his email pass with which Xmpp uses, and add the contact.
5. Omemo encryption | Now you can chat with someone using encryption
XMPP supports Omemo encryption. This means that if you activate the omemo encryption the messages will be encrypted, only you and the recipient will be able to read them, even those who have access to the server from where the messages pass (in this case autistici) will not be able to read them. Put simply: better if when this feature is activated! On Conversations, just click on the padlock at the top on a chat screen with someone. On Gajim (PC) it seems to me that you have to install the extension (from the menu at the top: Gajim-> Extensions, select Omemo, click on the square at the bottom to download it and install it)
6. Good chat!
Below other useful information ….
Set the ephemeral messages on your clients:
Ephemeral messages are messages that disappear over a certain time.
GAJIM: Click up on the Account menu -> Edit the accounts .. then select the account for which you want to activate ephemeral messages, select Privacy and here click on “Store” Conversations Chronology “then the duration of ephemeral messages.
Conversations: Click on the three points at the top right, then settings, then click on “Security”, then the last item at the bottom “Automatic deletion of messages”.
The ephemeral messages on the clients I have tried cannot be set differently for each individual chat (such as Whatsup, Telegram or Signal), but they can be set for every clients in a global way (same timing for all chats), yes we know, this can be uncomfortable.
Attention the management of ephemeral messages is managed totally differently compared to Signal/WhatsApp/Telegram. The disappearance of the messages is managed locally by its clients. This means for example that you have set up messages with disappear option to a day on your Android client, while on your Windows client you left the ephemeral messages deactivated … it will still appear all the complete chronology on your Windows client, while on yours Android client only messages related to the last day.
So, what do I recommend? If you want to have ephemeral messages you must manually set all your clients with active ephemeral messages (perhaps with the same temporality).
A note: if the person with I’m chatting has not set the ephemeral messages option, all the messages will remain on his client even if you have set all your clients in ephemeral messages! This is an important difference compared to the most famous software (Signal/Whatsup/Telegram), which must be kept in mind!
Gajim: Click on the menu at the top of Gajim -> preferences, then in the window on “Advanced”, then “Delete conversations chronology” Conversations: it doesn’t seem possible to us, in case you may be convenient to uninstall the app. For the individual chat it is very simple, just enter a chat, click on the 3 dots at the top right, then “empty the chronology”.
More common problems: can’t you see a private group they invited you?
This is sometimes solved by making the group send the invitation to the group while you are online. But be careful that seeing the invitation to the group in some clients is not one of the most intuitive things. On Gajim from Windows, a number appears on the symbol of your account on the bottom left, click on it and then you can accept the invitation. On Gajim from Linux a pop-up window should appear.
More common problems: can’t you write in a private group they invited you? You see users messages, but when you write and send the message it will return a window like this on the right.
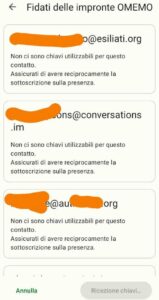
Let’s assume that private chats with OMEMO hardly work well with many participants who do not know each other.
The problem is that you can read messages and even write but if you send the message you are directed to a window where the key reception is disabled (see image on the right of Conversations).
As long as the users listed on the screen are not online so that they can exchange keys, you cannot send encrypted messages.
What the user can do is to write unencrypted (disabling OMEMO). For example, on Conversations just click the lock in the top right and select “clear”.
If you still want to write with the omemo encryption in a private group (not anonymous, therefore, with visible Jid) it is better that participants are contacts saved in the mutual address book and sign up for attendance. To do this, you have to go into the details of a contact and select “Send presence updates”, “Receive presence updates” (at least on Conversations/Cheogram calls them that). These “presence” options also contain OMEMO keys. This facilitates the correct exchange of keys (especially if some participants have multiple devices/clients and some of them are rarely online), but it is not mandatory, it could even be enough that they are online at the moment when the other one tries to write, so as to receive and exchange the key.
Another alternative strategy to being in each other’s addres books is to send a message without omemo at the beginning of the conversation, and then activate OMEMO later. If you want to use OMEMO encryption in the private group, it is recommended after the first messages to activate OMEMO encryption because if a participant is not contact of others and never writes encrypted, does not give others the possibility to understand which keys they use.
Most common issues: opening a chat from my new client, the messages are obscured
It’s normal, this happens because no one has ever been able to encrypt that particular device, which was still unknown.
Other more advanced XMPP knowledge:
XMPP (formerly “jabber”) is an XML-based messaging protocol -> XMPP: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XMPP,
The XEP are the XMPP extensions/plugins. Each server decides which XEP to use -> XEP: https://xmpp.org/extensions
OMEMO is the most used encryption on XMPP but there are other protocols of encryption of XMPP such as PGP and OpenPGP -> OMEMO: https://conversations.im/omemo
For work you need one server and at least two clients
– the server part needs to be hosted and maintained on a VPS or physical server -> for example the server (service) offered by https://www.autistici.org
– Clients are APP/programs that allow a user to connect to the XMPP network
XMPP is based on a federated structure. In short, there are many XMPP servers (like on Mastodon, emails etc.).
As well as a mail service, you have to have an account on a server that offers the XMPP service . There are many programs (clients) for XMPP because it is open source, anyone can create a program for xmpp.
So, everyone has to find their own server and client or create new ones.
Advanced notes: your clients may not be synchronized.
If you use the Autistici server, the various apps (clients) that you use are not synchronized with each other.
You might receive a message on your mobile app, but then if you go to the software you use on your computer you will not find the message. This is due to the fact that on the server of Autistici (other servers work differently such as disroot) messages are saved until the recipient reads them, after they are deleted.
To text with a person there is not only the autistici.org server, but there are also many other servers that once registered can provide you with an account (Jid). Here is a list of alternatives: https://providers.xmpp.net/ . If you are going to install Conversations, when you launch it for the first time and need to log in you also have the option to create a free jid from them.
Advanced notes: User contact = Jid
A user’s contact look like an email address, and is called “JID” (Jabber ID). Your JID is your identifier on the XMPP network. It’s like your email, but used for chat.
In xmpp two people can exchange messages without being contacts, that is included in the list of xmpp IDs known to their account (the so-called `roster`).
Inclusion in the contact list is always subject to approval of the candidate for inclusion, who may or may not agree to it. This also gives to the new contact the ability to see their online status (presence), and vice versa. Among the “presence” data to which you give access are also the OMEMO keys of your devices.
This kind of flexibility and confidentiality is generally unknown to other messaging systems, especially those that use the phone number as id and search in the telephone directory assigning anyone they find the status of contact.
XMPP supports OMEMO encryption. This means that if you activate the OMEMO encryption and the person with whom you are talking supports it, the messages will be encrypted, only you and the recipient will be able to read them, even those who have access to the server where the messages pass (in this case Austici.org) will not be able to read them. In simple words: better if you activate this feature when chatting!
To read each other with OMEMO encryption two users need to exchange keys or called “Fingerprints”.
A user has an Omemo key or fingerprint for each client he uses.
Groups in XMPP are called muc (multi-user-chat).
The private groups that are created are not anonymous because they show user addresses (Jid), so each participant can see the addresses of all other/patecipant* users.
Semi-anonymous groups (or completely anonymous, but there is no possibility to moderate) are public groups where only the admins know the jid of others.
This preserves your privacy.
Since you do not know the jid of participants, you can’t share keys/presence, so it is not activable omemo encryption.
When you create a Public Channel, you can set it in different ways, the owner of the channel can assign various roles to those who subscribe to the channel and can also decide that the only one allowed to write is himself (as on Telegram channels).
Documentation on xmpp
Last update: 29/11/2025